Fly Life Cycle

The life cycle of a fly includes four key stages: egg, larva (maggot), pupa, and adult. This metamorphosis isn’t just interesting biologically; it’s also crucial to effective fly pest control. The early signs of an infestation can be identified by understanding how flies reproduce and develop, and the right prevention and fly treatment strategies can be applied at every stage.
Whether you’re dealing with a housefly problem or managing a fruit fly infestation, knowing how these insects develop is the first step to breaking the cycle.
The life cycle of a fly
Flies’ lifespan is relatively short. They usually live around 15-30 days. Similar to other insects, within this period, they go through four life cycle stages – fly egg, larva, pupae and adult. 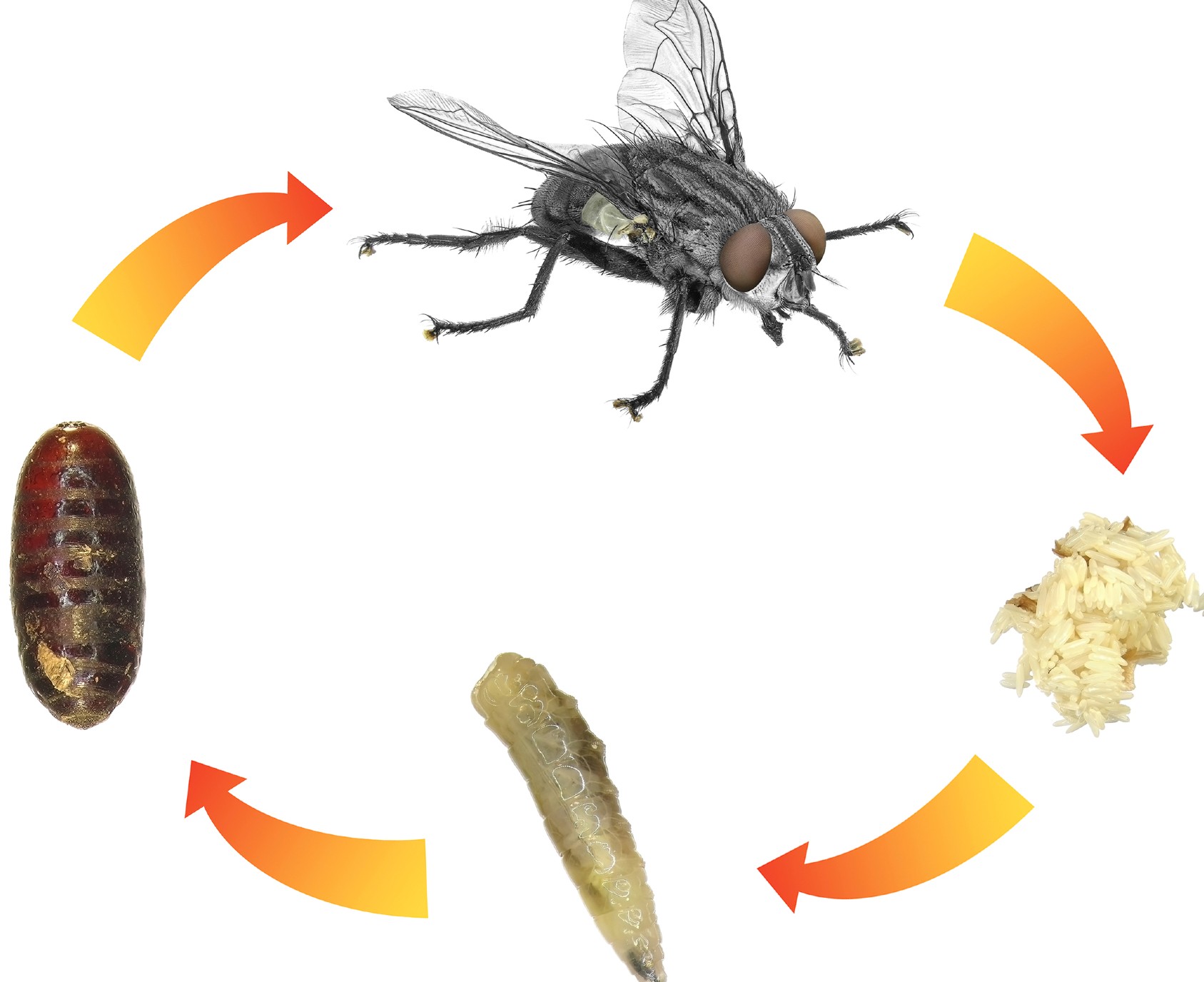
Fly eggs
The first stage of the fly life cycle is the egg. After mating, the female flies lay eggs and the male ones fertilise them. Flies lay their eggs in warm, moist spaces, usually on decaying organic matter such as food waste, garbage, carrion, animal or human faeces.
Fly larvae
The second stage of the fly life cycle is the larva, also known and referred to as the maggot. Fly larvae are worm-like in shape and pale in colour. They stay close to their source of food and feed best when on animal corpses, manure and garbage. Maggots eat in order to grow and begin their moulting process. This is essentially the process of insects shedding their skin or their exoskeleton. This happens when a new skeleton beneath has been fully developed. The moulting period in flies happens three times before the fly enters its next life cycle stage.
Fly pupae
After the final moulting, the larva enters the pupa stage. During this stage, flies are usually dormant – do not move and do not feed. They develop a cocoon-like shell and grow their wings, antennas and legs. Once they break out of their shell, flies are fully grown and now in their adult form.
Read more: Types of Flies in the UK
Where do flies lay eggs?
Flies usually lay their eggs on moist, decaying organic matter, such as food waste, carrion or faeces. They are white and elongated, normally around 0.05 inches long. Fly eggs take between 8 and 20 hours to hatch.
How do flies reproduce?
Despite their short lives of usually 15-20 days, flies’ reproduction is significant. They start multiplying very early. The mating process is initiated by the male fly and begins with a short courtship. The female fly produces eggs, which are then fertilised by the male. The entire mating process can last from 30 minutes to 2 hours. The female fly finds a warm, moist area with enough food around to lay the fertilised eggs.
Where do flies come from?
Flies could come from anywhere where there is decaying organic material – e.g. manure, food waste, general garbage, etc. They prefer warm weather and thrive in temperatures between 17-32℃. With the rate of reproduction, they can easily cause an infestation. This is a huge problem since flies can transmit a number of diseases and are very unhygienic.
Restaurants risk food safety issues because of flies’ breeding and feeding habits. Flies multiply fast when there’s plenty of food and a warm environment. You need to keep flies away from your restaurant. It’s easy for flies to ruin a restaurant’s reputation. Commercial kitchens generate food odours that attract fruit flies, drain flies, and house flies. The control of pests in restaurants is an essential part of the business.
Read more: How to Get Rid of Flies?
How long is the life cycle of a fly?
The complete life cycle of a common housefly typically spans between 7 to 10 days, though this can vary depending on environmental conditions such as temperature, humidity, and food availability. Here’s a breakdown of each stage:
- Egg stage: Flies lay clusters of eggs, usually around 75-150 at a time, which hatch within 8 to 24 hours.
- Larva (maggot) stage: The larvae feed on organic matter for 3 to 5 days, rapidly growing and shedding skin as they mature.
- Pupa stage: After feeding, the maggots enter the pupal stage, encasing themselves in a hardened shell for another 3 to 6 days.
- Adult stage: A fully developed fly emerges, ready to mate within 24 hours and begin the cycle anew.
In ideal warm environments, this cycle can complete in just a week, leading to rapid population growth.
Where do flies lay eggs in the house?
Flies are opportunistic breeders and prefer warm, moist, and decaying organic material as egg-laying sites. In the average household, the most common places where flies lay eggs include:
- Bin areas and food waste containers
- Kitchen drains and compost bins
- Pet waste left indoors or in gardens
- Soiled nappies or damp cloths
- Rotting fruit or meat
Female flies are capable of detecting the presence of fermenting substances and decomposing materials even in the smallest crevices, making regular hygiene and waste disposal practices essential.
What do flies eat?
Flies are definitely not picky and will eat almost anything. They are attracted to decaying organic materials such as overripe fruits and vegetables, human and animal faeces, manure, oozing wounds, etc. They especially love sugary substances. In order to prevent an infestation, you should not leave any food unattended and store everything properly. Do not leave waste of any sorts for a long time inside or outside of your property and keep all premises in good hygienic condition.
How do flies die?
Houseflies live between 15-30 days. The female flies generally live longer, around 25-30 days, while the males live around 15 days. In some cases, their lives can be prolonged by cooler climate conditions, when it usually takes more time for them to fully grow and go through their full life cycle. They sometimes hibernate during winter. In the best-case scenario, a fly can stay alive for around two whole months. That is if it doesn’t enter the wrong house and get killed prematurely.
Houseflies can also die from stress if they find themselves in a closed indoor space. They get disoriented and can die while trying to get out. These insects are not adapted to live in air-conditioned spaces, which could also result in their death.
How to get rid of fly larvae?
Eliminating fly larvae requires a multi-pronged approach aimed at both destroying existing maggots and removing breeding grounds. Follow these steps for effective fly larva control:
- Locate the breeding source: Inspect bins, drains, food storage, and hidden organic matter.
- Physically remove larvae: Use gloves and dispose of infested material in sealed bags.
- Clean and disinfect: Wash the affected area with hot water and a disinfectant to remove any residual organic matter.
- Use larvicides: Apply commercial fly larva killers or natural alternatives like diatomaceous earth or boiling water with vinegar in drains and compost bins.
- Install fly traps: To capture adult flies and prevent further egg-laying.
Regular waste disposal, deep cleaning of potential fly habitats, and sealing entry points will significantly reduce the chances of future infestations.
Conclusion
Houseflies are the most commonly known fly type in the world. Their life cycle includes four stages – egg, larva, pupae and adult fly. Flies live between 15-30 days and multiply in great numbers. One female fly can lay over 500 eggs in her lifetime. Since flies generally prefer to eat decaying organic materials, reproduce extremely fast and transmit food-borne diseases, they are considered pests. So, if you have flies infestation we recommend hiring a professional fly exterminator who will use highly effective insecticide or other methods for long-lasting results.
Are there flies in your home?
Note that we only aim to provide some useful information about how to identify flies in each stage of their life.











